Read Time:3 Minute, 32 Second
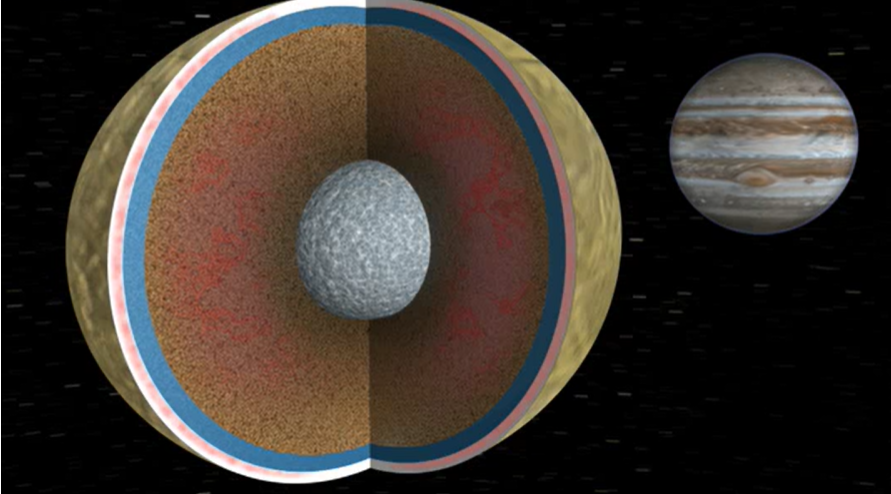
IntroductionNASA’s Study on Tidal Forces: Unlocking the Secrets of Planetary and Lunar Interiors
- The Role of Tidal Forces in Celestial Mechanics: An introduction to tidal forces, how they arise in space, and why they’re crucial for understanding planetary and lunar geology.
- NASA’s New Approach to Modeling Non-Spherical Bodies: How NASA’s innovative approach breaks new ground by accounting for non-spherical interiors, providing insights beyond the traditional, spherical-based models.
Fundamentals of Tidal Forces and Their Effects on Celestial Bodies

- What Are Tidal Forces? A breakdown of how gravitational interactions between celestial bodies create tidal forces and affect their orbits, rotation, and internal structures.
- Differences Between Traditional and New Models: Contrast the assumption of spherical symmetry in older models with NASA’s non-spherical approach, explaining why irregularly shaped bodies yield new insights.
Europa as a Prime Example: Tidal Forces in Action
- Overview of Europa’s Structure and Surface: Describe Europa’s icy shell, suspected liquid ocean, and rocky core, providing context for how tidal forces impact its interior.
- Europa’s Unique Orbital Path and Eccentricity: Explain how Europa’s slightly elliptical orbit around Jupiter causes varying tidal forces, leading to flexing of its interior.
- Mechanics of Tidal Heating in Europa: Describe how tidal forces generate frictional heating in Europa’s subsurface, possibly keeping its ocean in a liquid state.
- Role of Tidal Forces in Potential Habitability: Expand on the theory that tidal heating may support microbial life, possibly by maintaining liquid water beneath the ice shell.
The Science Behind Tidal Heating: How and Why It Works
- Tidal Kneading and Frictional Heating Explained: Explain the process of tidal “kneading” due to gravitational forces and how it leads to heat generation, using analogies like the bending of a paperclip.
- Impacts on Europa’s Internal Structure and Ice Shell: Discuss how this heating affects Europa’s geological layers, potentially causing cracks in the ice and leading to geysers or plumes.
- Energy Sources and Life Potential: Analyze how tidal heating could supply necessary energy to sustain life forms and create stable ecosystems in the subsurface ocean.
Beyond Europa: Exploring Tidal Effects in Other Celestial Bodies
- Tidal Forces in Other Moons and Planets: Broaden the discussion to other moons like Enceladus and Titan, which may also experience tidal heating, and discuss any evidence for subsurface oceans.
- Examples from the Solar System and Exoplanets: Highlight moons and planets where tidal effects may be key to understanding geological activity and potential habitability.
- Implications for Exoplanetary Research: How knowledge of tidal forces on distant exoplanets could guide the search for habitable zones outside our solar system.
Innovative Methodology in NASA’s Study: Moving Beyond Spherical Models
- Non-Spherical Interior Modeling Explained: A more technical exploration of the non-spherical models NASA developed, explaining how they account for irregular shapes and more complex internal dynamics.
- Applications in Seismology and Planetary Geology: Discuss how this methodology can enhance predictions about volcanic activity, seismic movements, and crustal shifts in distant celestial bodies.
- Impact on Future Space Missions and Instrumentation: Describe the implications for mission planning, including instruments that could detect tidal effects and heat signatures on Europa and similar bodies.
Astrobiological Implications: How Tidal Heating Affects the Search for Life
- Prerequisites for Life and Tidal Heating’s Role: Define the conditions necessary for life and how tidal heating meets these needs by providing liquid water, energy, and stable conditions in otherwise hostile environments.
- Current and Future Missions to Detect Life on Europa: Discuss upcoming missions, such as NASA’s Europa Clipper, and how they aim to detect biosignatures or conditions that could support life.
- Broadening the Habitable Zone Concept: How findings from tidal studies challenge the conventional habitable zone theory, proposing new areas where life may exist outside Earth-like conditions.
Conclusion
- Summary of NASA’s Contribution to Planetary Science: Recap the significance of NASA’s study, emphasizing its groundbreaking approach to understanding non-spherical bodies.
- Future Directions for Tidal Force Research: Speculate on how this study could influence future planetary exploration and our understanding of celestial bodies.
- Final Thoughts on Tidal Heating and Life Beyond Earth: Conclude with reflections on how tidal forces and internal heating are expanding the scope of habitable environments in our universe.
Average Rating